Struggling with focus, sleep, or brain fog?
Have you tried generic magnesium and felt little difference? Not all magnesium forms work the same. If your goal is cognitive support and better sleep architecture, the specific chelate you choose matters.
TL;DR
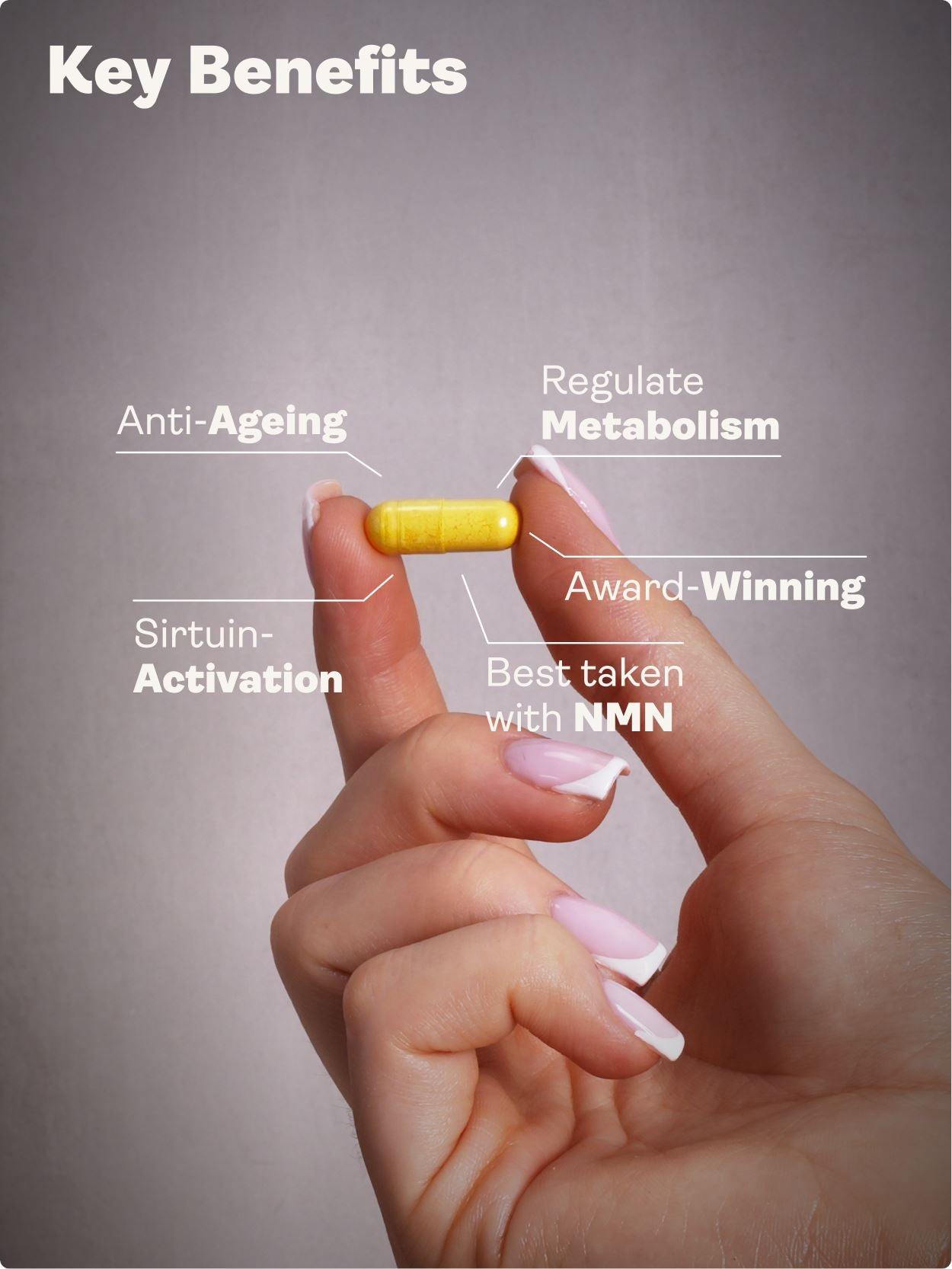
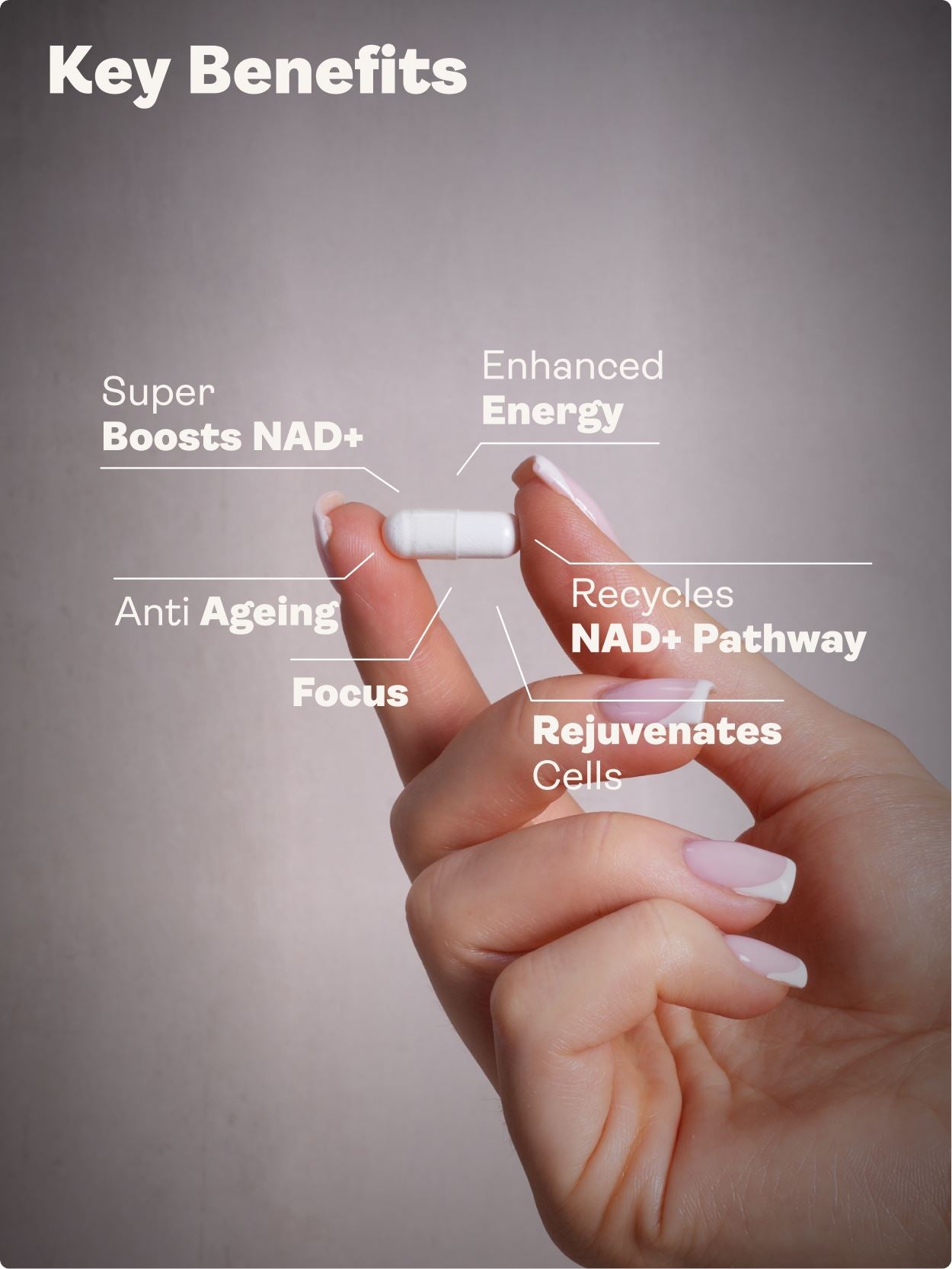
Magnesium L-Threonate (magnesium threonate) is a chelated form discovered in 2010 that pairs magnesium with L-threonic acid. It is designed to increase brain magnesium more effectively, which may benefit memory, learning, mood, stress responses, and sleep quality. It may also assist muscle relaxation and recovery via mitochondrial and calcium-channel effects. For most adults, consistent daily use for 4–12 weeks is needed before meaningful cognitive or sleep changes are noticed. A nutrient-dense diet, good sleep hygiene, and regular exercise amplify results. In a longevity and anti-ageing context, magnesium L-threonate can complement broader biohacking strategies that prioritise brain health across the lifespan.
What is Magnesium L-Threonate?
Magnesium L-Threonate (often shortened to magnesium threonate) is a patented chelate pairing magnesium with L-threonic acid, a vitamin C metabolite. Chelation improves stability and absorption characteristics. Crucially, this form was engineered to elevate magnesium specifically in the brain, an organ protected by a tight blood–brain barrier (BBB).
Magnesium as a mineral underpins over 300 enzymatic reactions involved in ATP production, DNA repair, protein synthesis, and neuronal signalling. Yet dietary shortfalls are common in Western diets, compounded by low vitamin D status and age-related renal losses. When brain magnesium runs low, people may notice forgetfulness, low mood, anxiety, poor stress tolerance, or unrestorative sleep.
Why target the brain? Blood–brain barrier, bioavailability, and synaptic plasticity
Most magnesium salts (e.g., oxide) are poorly absorbed or act primarily in the gut. Some gentler chelates (e.g., glycinate) improve systemic absorption but still struggle to raise brain levels. Magnesium L-threonate was designed for higher brain bioavailability, with studies indicating superior uptake and retention relative to several common forms.
In preclinical work, increasing brain magnesium enhanced synaptic plasticity—the ability of neural connections to strengthen or adapt—which underlies learning and memory consolidation. Human data has shown improvements on standardised cognitive assessments in healthy adults after sustained use. The signal appears stronger in older individuals, aligning with age-related declines in brain magnesium and plasticity.
Science Snapshot: Key findings at a glance
- Higher brain delivery: Magnesium threonate elevates brain magnesium more effectively than several other magnesium forms in comparative models.
- Memory & learning: Healthy adults supplementing daily for ~30 days showed better performance on memory tests versus placebo, with larger gains in older participants.
- Neuroprotection: In hypoxia models, magnesium threonate reduced neuronal death and preserved cognitive function; in Parkinson’s models, it supported dopaminergic cell integrity and motor metrics.
- Stress & mood: By modulating GABA and glutamate signalling and influencing stress hormone responses, it may help with anxious mood and stress resilience.
- Sleep architecture: Magnesium affects GABAergic tone and melatonin pathways, with supplementation associated with improved sleep quality, shorter sleep latency, and healthier REM dynamics.
- Muscle recovery: Magnesium supports mitochondrial efficiency and calcium handling in muscle, potentially easing cramps and aiding recovery.
Potential benefits: memory, mood, sleep, and recovery
Cognitive support (memory, learning, mental clarity)
By raising brain magnesium, this form can support synaptic plasticity, long-term potentiation, and the cellular foundations of memory. Human data in healthy adults showed improved memory scores after a month, with older participants benefiting most. In practical terms, users often describe better recall, easier learning, and less mental “static.”
Mood and stress responses
Magnesium participates in neurotransmitter balance—enhancing inhibitory GABA tone while tempering excess glutamatergic activity. This can translate into calmer mood, fewer stress spikes, and smoother cognitive performance under pressure. Supporting the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis may also help with perceived stress.
Sleep quality and efficiency
Magnesium is involved in melatonin synthesis and GABAergic signalling, both relevant to initiating and maintaining sleep. Supplementation has been associated with improved total sleep time, sleep efficiency, shorter sleep latency, and more refreshing sleep. Many people notice that evening dosing pairs well with their wind-down routine.
Muscle relaxation and recovery
Magnesium helps regulate calcium influx into muscle cells, easing unnecessary contraction and cramping. By supporting mitochondrial ATP generation, it may assist post-exercise recovery. This can be meaningful for active individuals or those with nighttime leg discomfort that disrupts sleep.
Biohacking, longevity, and healthy ageing: Targeting brain magnesium aligns with a broader healthy-ageing strategy that emphasises cognitive reserve, stress resilience, and sleep optimisation. As part of a holistic protocol, magnesium L-threonate can complement nutrition, strength training, circadian alignment, and other brain-forward habits associated with longevity and anti-ageing outcomes.
How it works: mechanisms you can act on
- BBB permeability: The threonate ligand facilitates transport that elevates brain magnesium more effectively than several common forms.
- Synaptic plasticity: Higher brain magnesium supports NMDA receptor regulation and long-term potentiation, key to learning and memory.
- Neurotransmitter balance: Enhances inhibitory GABAergic tone and helps modulate excitatory glutamate signalling for calmer neural networks.
- Melatonin & sleep: Contributes to melatonin pathway efficiency and sleep architecture, notably REM and sleep onset latency.
- Mitochondria & muscle: Supports ATP synthesis and calcium handling in muscle tissue, relevant for performance and recovery.
How magnesium threonate compares to other forms
| Form | Main Strength | Common Uses | GI Tolerance | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magnesium L-Threonate | Higher brain bioavailability | Cognition, sleep quality, stress resilience | Generally good | Often requires consistent use (4–12 weeks) for cognitive effects |
| Magnesium Glycinate | Gentle, well-absorbed | General magnesium repletion, calm | Excellent | Great systemic option, less BBB-targeted |
| Magnesium Citrate | Budget, well-studied | General use; bowel regularity | May loosen stools | Useful for occasional constipation |
| Magnesium Oxide | High elemental content | Budget | Lowest absorption; GI upset possible | Less efficient for repletion |
| Magnesium Malate | Energy support (malate cycle) | Daytime energy, muscle comfort | Good | Pairs well with training blocks |
Who might consider magnesium threonate?
- Adults seeking support for memory, learning, or mental clarity.
- Individuals with stress-related sleep issues or difficulty unwinding at night.
- Active people or those with muscle cramps looking for better recovery.
- People improving overall nutrient sufficiency as part of a healthy ageing plan.
Note: Discuss supplementation with your clinician if you have medical conditions or take medications (see interactions below).
How to use it: dosing, timing, stacking, and timelines
Suggested dosing & timing
- Common amount: 1,000–2,000 mg magnesium L-threonate daily (supplying ~144 mg elemental magnesium) is a typical research-informed range for adults.
- Split doses: Morning + evening is common; many prefer an evening-weighted dose for sleep support.
- With food: Taking with meals can reduce occasional GI discomfort.
When to expect results
- Short term (1–2 weeks): Some notice calmer mood or better wind-down.
- 4–8 weeks: Early changes in recall, sleep quality, and stress tolerance are more likely.
- 8–12+ weeks: Cognitive effects tend to consolidate; continue consistent use for full benefit.
Smart stacking (optional)
- Sleep routine: Pair with a regular bedtime, low evening light, and a cool, dark room.
- Diet quality: Emphasise leafy greens, legumes, seeds, fish, and adequate protein to support neurotransmitter balance and recovery.
- Training: Resistance training 2–3× weekly improves brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and sleep depth, complementing magnesium’s effects.
Quality matters: Choose products that disclose elemental magnesium per serving and undergo third-party testing. Youth & Earth Magnesium Threonate is formulated to support cognitive performance, sleep quality, and recovery as part of a broader healthy-ageing routine.
Safety, side effects, and interactions
Magnesium threonate is generally well tolerated. Possible effects—more likely at higher intakes—include loose stools, mild nausea, or stomach cramping. Taking with food and splitting doses often resolves these issues. Rarely, sensitive individuals may notice lightheadedness if blood pressure dips; reduce dose and consult a professional if this occurs.
Medication interactions
- Antibiotics: Magnesium can reduce absorption of certain antibiotics; separate dosing by several hours.
- Thyroid medications: Take magnesium several hours apart to avoid interference.
- Bisphosphonates and PPIs: Discuss timing with your prescriber.
- Diuretics: Can alter magnesium balance; monitor with your clinician.
Always consult your healthcare provider before starting supplements, especially if you have kidney disease, cardiovascular conditions, or are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Conclusion & checklist
Magnesium L-Threonate stands out for its brain-first design. By elevating brain magnesium, it supports memory, learning, calmer mood, and more restorative sleep while also aiding muscle relaxation and recovery. It is a practical addition to a lifestyle that prioritises nutrition, movement, and circadian health—core pillars for healthy ageing and, for many, a measured biohacking approach.
Quick checklist
- Define your goal: memory, sleep, stress, recovery—or a combination.
- Choose a third-party tested formula that discloses elemental magnesium.
- Start at the low end; split doses with meals; consider evening emphasis for sleep.
- Commit to 8–12 weeks of consistent daily use before judging results.
- Support with protein-rich, nutrient-dense eating; train 2–3× weekly; protect your sleep window.
- Review medications with your clinician to optimise timing and safety.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is magnesium threonate better than other forms for the brain?
It was developed to raise brain magnesium more effectively than many common forms and has evidence linking sustained use with memory benefits. For systemic repletion or bowel regularity, other forms may be preferable. Choose based on your primary goal.
How long until I notice effects?
Plan on 4–8 weeks for noticeable changes in memory or sleep, with full effects often requiring 8–12 weeks. Mood and wind-down benefits may appear sooner in some people.
Can I take it with other magnesium types?
Yes, many people use a small evening dose of threonate for brain support and a systemic form (e.g., glycinate) earlier in the day. Track total elemental magnesium and your personal tolerance.
Does it help with anxiety or stress?
By supporting GABAergic tone and modulating stress responses, it may assist with a calmer baseline. For persistent symptoms, partner with your healthcare provider.
What if I get digestive upset?
Reduce the dose, take with food, and consider split dosing. If symptoms persist, discontinue and consult a professional.
Glossary
- Blood–brain barrier (BBB): A protective barrier that tightly controls what reaches brain tissue.
- Chelation: Binding a mineral to an organic molecule to influence absorption and distribution.
- Elemental magnesium: The actual amount of magnesium in a supplement dose, excluding the weight of the chelate.
- GABA: An inhibitory neurotransmitter that helps calm neuronal activity.
- Synaptic plasticity: The capacity of neural connections to strengthen or weaken over time, central to learning and memory.