TL;DR
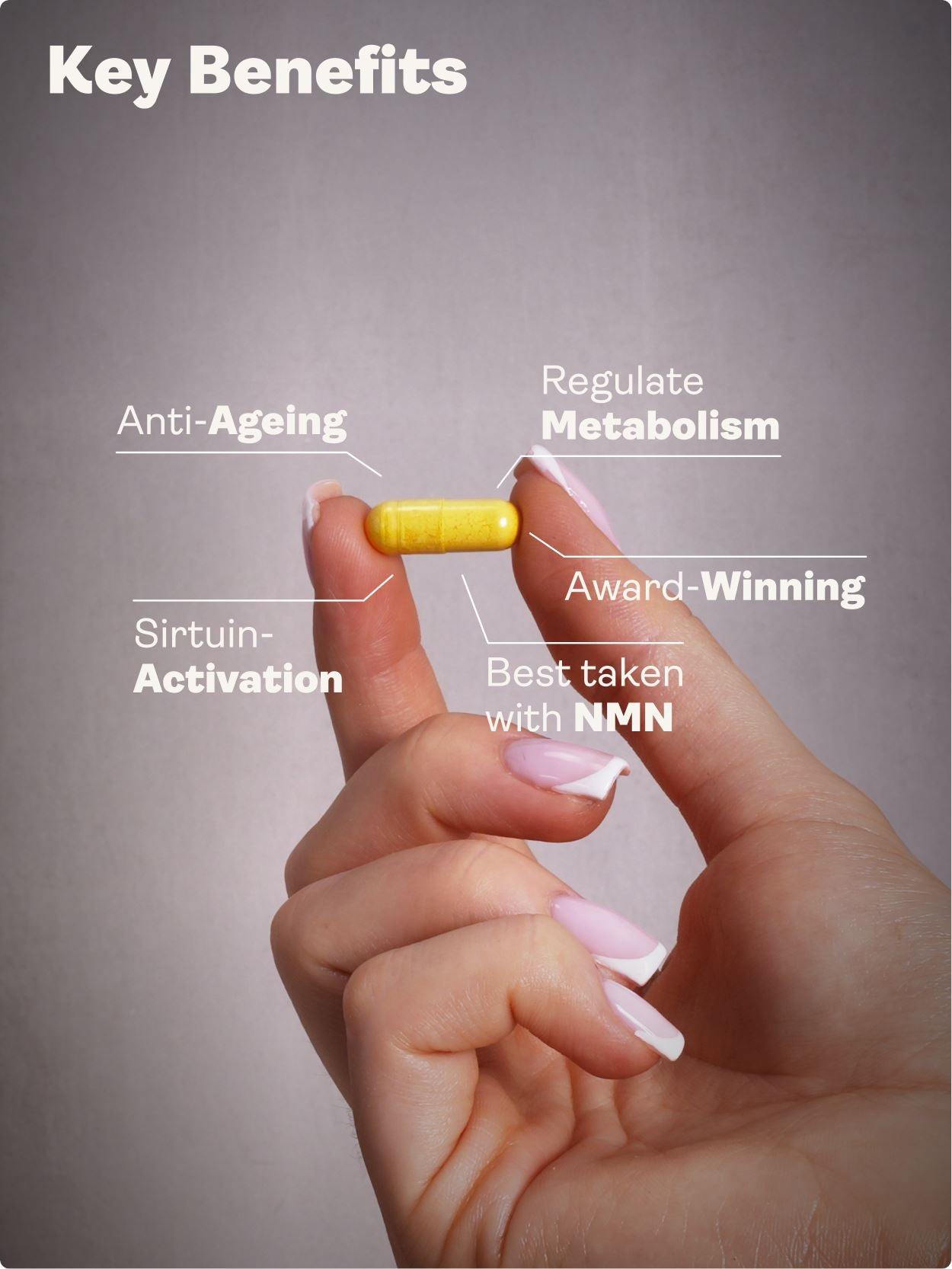
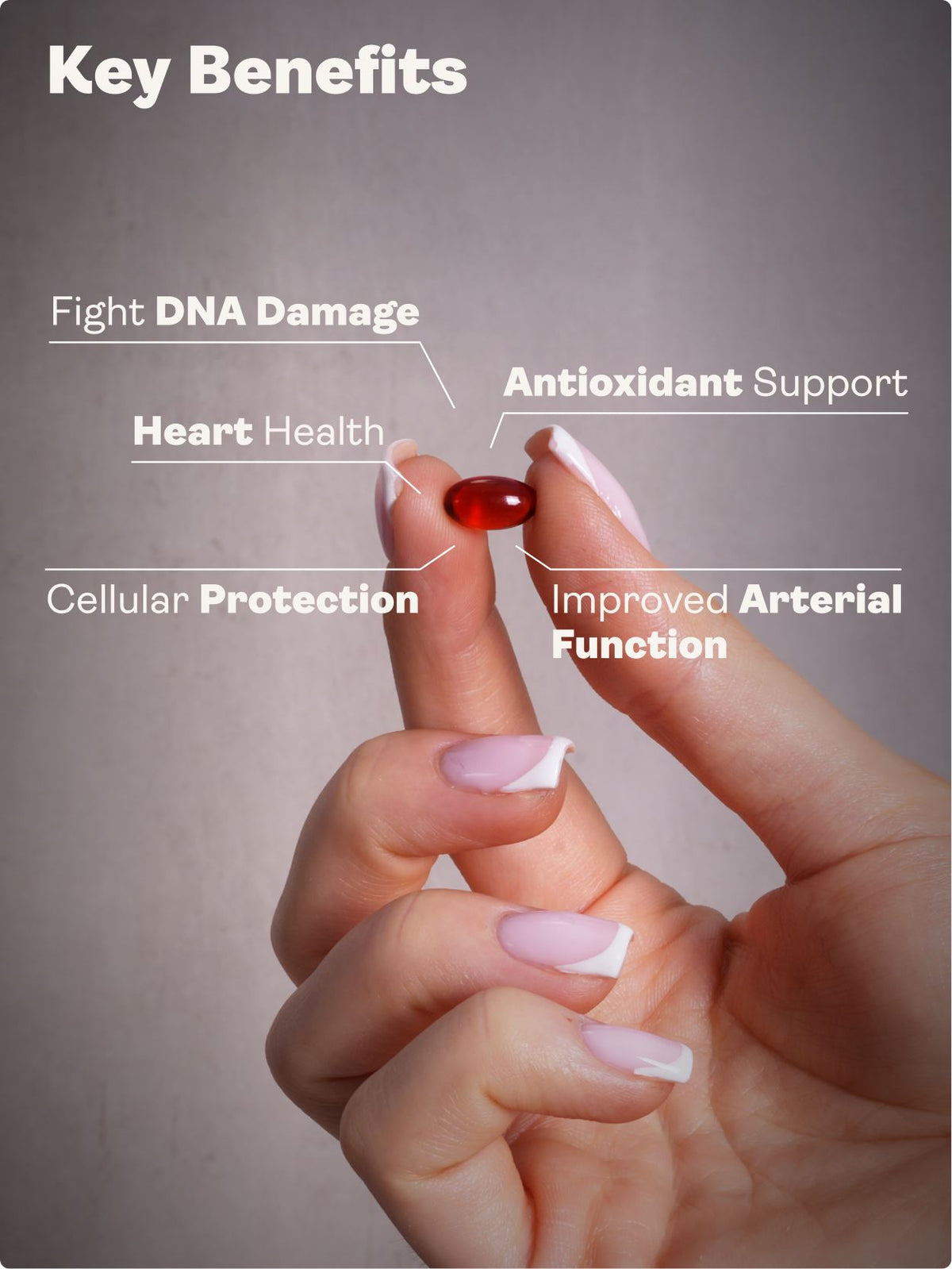
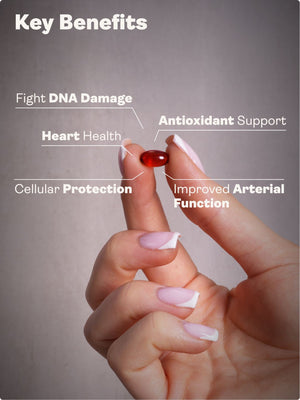
Annatto tocotrienols are a potent and bioavailable form of vitamin E with superior antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, cholesterol-lowering, and cancer-fighting properties. Free from alpha-tocopherol (which interferes with their function), annatto-derived tocotrienols—especially the delta and gamma isomers—support cardiovascular health, liver function, metabolic resilience, immune regeneration, DNA repair, and skin protection. Backed by over 20 years of research, they are now available in tocopherol-free formulations like Youth & Earth's Tocotrienols EAnnato Delta Gold.
Table of Contents
What Is Vitamin E, Really?
For decades, the term "vitamin E" was synonymous with alpha-tocopherol. This lipid-soluble nutrient earned its reputation as an antioxidant and skin-rejuvenator. But vitamin E has two families: tocopherols and tocotrienols—each with four isomers (alpha, beta, gamma, delta).
Most conventional supplements contain only alpha-tocopherol. Yet research now reveals that the other half—tocotrienols—may be the real powerhouse, especially when sourced from annatto.
Tocotrienols vs Tocopherols: What’s the Difference?
| Feature | Tocopherols | Tocotrienols |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Saturated tail | Unsaturated tail |
| Mobility in Membranes | Slow | Fast |
| Antioxidant Potency | Moderate | Up to 50x higher |
| Cholesterol Lowering | Weak | Strong (via HMG-CoA inhibition) |
| Cancer-Fighting | Minimal | Multi-pathway inhibition |
| Presence in Diet | Widespread | Rare |
| Tocopherol Interference | N/A | Suppressed when tocopherols present |
Tocopherols act like local police—effective but slow. Tocotrienols are state troopers: agile, fast-acting, and far-reaching.
Where Do Tocotrienols Come From?
Tocotrienols occur in nature, but they're rare and often contaminated by tocopherols.
| Source | Tocotrienol Content | Tocopherol Content | Tocopherol-Free? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Palm Oil | ~75% | ~25% (mostly alpha) | No |
| Rice Bran | ~50% | ~50% | No |
| Wheat Germ | Low | High | No |
| Annatto | 100% (gamma & delta) | ~0% | Yes |
Only annatto provides pure tocotrienols without alpha-tocopherol, making it the gold standard.
How Was Annatto Tocotrienol Discovered?
In 2002, Dr. Barrie Tan was studying carotenoids in the Amazon when he encountered annatto, the lipstick-red seedpod used in traditional dyes. Expecting to find beta-carotene, he instead uncovered pure delta- and gamma-tocotrienols—with zero tocopherol content.
This discovery triggered over 20 years of clinical research validating annatto tocotrienols in:
-
Cancer therapy
-
Fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
-
Osteopenia
-
Cardiovascular health
-
DNA damage reversal
Why Choose Annatto as a Tocotrienol Source?
-
No tocopherol interference
-
Contains only gamma and delta, the two most potent isomers
-
Naturally derived—no chemical fractionation needed
-
Backed by dozens of clinical trials
-
Sustainable and potent
Youth & Earth uses this exact source in Tocotrienols EAnnato Delta Gold, delivering:
-
90% Delta-Tocotrienol
-
10% Gamma-Tocotrienol
Delta vs Gamma Tocotrienols
| Isomer | Primary Actions | Target Pathways |
|---|---|---|
| Delta | Apoptosis, LDL reduction, liver fat clearance | NF-κB, HMG-CoA, IL-6 |
| Gamma | Anti-inflammatory, anti-angiogenic, metabolic modulation | COX-2, Raf/MEK/ERK, SREBP |
Both work synergistically but have distinct cellular roles.
What Makes Tocotrienols Unique as Antioxidants?
Tocotrienols:
-
Penetrate cell membranes faster
-
Localise in key organelles (mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum)
-
Inhibit lipid peroxidation
-
Regenerate endogenous antioxidants like glutathione
Compared to tocopherols, they:
-
Neutralise more ROS per molecule
-
Protect broader tissue types (brain, heart, liver)
How Do Tocotrienols Work in the Body?
They function through multiple mechanisms:
-
HMG-CoA Reductase Degradation: reduces LDL cholesterol
-
SREBP Downregulation: lowers lipid biosynthesis
-
Ceramide Synthesis: induces tumour suppression
-
NF-κB Inhibition: lowers inflammation
-
MMP-9 & ICAM-1 Reduction: blocks metastasis
Are Tocotrienols Bioavailable?
Yes—but they require dietary fat for optimal absorption. Once ingested:
-
They dissolve into lipid micelles
-
Transported via lymph to the liver
-
Redistributed via lipoproteins to tissues (brain, heart, skin, liver)
Peak plasma levels occur within 2–5 hours. Unlike tocopherols, they rapidly exit the bloodstream and deposit in organs, enhancing functional bioavailability.
Why Avoid Tocopherols with Tocotrienols?
Tocopherols—especially alpha—inhibit tocotrienol function via:
| Interference Mode | Outcome |
|---|---|
| Blocks Absorption | Lower plasma levels |
| Displaces in Tissues | Reduced antioxidant effects |
| Depletes Storage | Limits duration of action |
| Inhibits Cancer Pathways | Blocks apoptosis, angiogenesis |
| Antagonises Cholesterol Reduction | Counters HMG-CoA inhibition |
Always choose tocopherol-free tocotrienols.
Can Tocotrienols Help Combat Cancer?
Yes—across multiple mechanisms:
Cancer-Fighting Mechanisms
| Mechanism | Function | Target | Isomer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apoptosis | Induces cell death | NF-κB | Delta |
| Checkpoint Inhibition | Slows cell cycle | STAT3, Cyclin D1 | Gamma |
| Angiogenesis Blockade | Inhibits new blood vessel growth | Raf/MEK/ERK | Delta, Gamma |
| Metastasis Suppression | Limits spread of cancer | MMP-9, ICAM-1 | Gamma |
| Chemoprotection | Reduces side effects of chemotherapy | Epirubicin Toxicity | Delta |
What Are the Health Benefits of Tocotrienols?
| System | Effects |
|---|---|
| Cardiovascular | Reduces LDL, lowers arterial stiffness |
| Liver | Improves NAFLD, lowers ALT, reverses fibrosis |
| Metabolic | Suppresses fat cell formation, improves insulin sensitivity |
| Immune | Reverses immune senescence, reduces cytokine storms |
| Bone | Prevents osteoporosis, improves calcium retention |
| Brain | Protects against oxidative neurodegeneration |
| Skin | Reduces photoageing, improves elasticity |
| Inflammation | Inhibits NF-κB, COX-2, and inflammatory cytokines |
Do Tocotrienols Combat Ageing?
Yes. Tocotrienols:
-
Improve DNA stability
-
Reverse immune decline (senescence)
-
Lower arterial stiffness
-
Improve mitochondrial performance
-
Increase skin collagen and moisture
In one study, 160 mg/day of tocotrienols reversed DNA damage in older adults in 3 months.
Recommended Dosage and Timing
| Goal | Dosage | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Cardiovascular | 200–300 mg/day | Take with fats |
| Liver (NAFLD) | 250–600 mg/day | Divided doses |
| Cancer Support | 400–600 mg/day | With oncologist support |
| Anti-Ageing | 100–200 mg/day | Long-term use beneficial |
| General Wellness | 100–150 mg/day | Maintenance phase |
Best taken with a fatty meal (olive oil, avocado, nuts).
Conclusion: Why We Recommend Annatto Tocotrienols
Annatto tocotrienols offer:
-
Superior antioxidant effects
-
Better bioavailability
-
Proven support for heart, liver, skin, and longevity
-
No tocopherol interference
Youth & Earth’s Tocotrienols EAnnato Delta Gold contains:
-
90% Delta-Tocotrienol
-
10% Gamma-Tocotrienol
-
100% Tocopherol-Free
-
Derived from Annatto Bean
If you’re looking for a next-generation vitamin E that goes beyond the basics, annatto tocotrienols are your answer.
FAQs
Q: Can I take tocotrienols with fish oil or other fats?
Yes—healthy fats enhance absorption.
Q: Are tocotrienols suitable for vegans?
Yes, if derived from annatto and encapsulated appropriately.
Q: Can I take them with tocopherols?
It’s best to avoid co-administration due to functional interference.
Q: Are there side effects?
Tocotrienols are well-tolerated in clinical studies up to 600 mg/day.
Glossary
-
Tocotrienols – Unsaturated members of the vitamin E family
-
Tocopherols – Saturated vitamin E forms, commonly used in supplements
-
NF-κB – A protein complex involved in inflammation and cancer
-
HMG-CoA Reductase – Enzyme involved in cholesterol synthesis
-
SREBP – Proteins that regulate lipid homeostasis
-
Annatto – A red plant from the Amazon rainforest rich in tocotrienols